Muscle Over 40: Age-Defying Tips
As we age, maintaining muscle mass becomes increasingly important for overall health and well-being. However, many people believe that building muscle is only for the young, and that as we get older, our muscle mass naturally deteriorates. But is this really true? In this blog post, we will explore the impact of age on muscle mass, the role of weightlifting in aging muscles, weightlifting tips for the elderly, nutrition and recovery strategies, creating a tailored workout plan, long-term health optimization tips, and whether age is just a number in weightlifting. So, if you're over 40 and looking to defy the effects of aging on your muscles, keep reading!
Age and its Impact on Muscle Mass
As we age, there are several factors that can contribute to the loss of muscle mass. One of the main factors is changes in hormone levels, specifically a decrease in testosterone production. Testosterone plays a crucial role in building and maintaining muscle mass, so lower levels of this hormone can result in muscle loss.
In addition, older lifters training might find that their muscle fibers diminish with age, which can impact strength and mobility. Muscle fibers are responsible for generating force and power, and as they decrease, it becomes harder to maintain muscle mass and strength.
muscle

Understanding Muscle Deterioration with Age
Muscle deterioration, also known as muscle atrophy, occurs naturally as we age. This process involves the loss of muscle mass and strength, and can be accelerated by factors such as a sedentary lifestyle or certain medical conditions.
Middle aged weight lifting, specifically resistance training, can be highly effective in offsetting muscle loss and enhancing mobility. By engaging in weightlifting exercises, older individuals can stimulate muscle growth and maintain their overall strength.
Additionally, hormone levels play a significant role in muscle deterioration. As we age, our hormone production decreases, which can further contribute to muscle loss. However, research has shown that resistance training can help boost hormone levels, such as testosterone, even in older individuals.
The Role of Weightlifting in Aging Muscles
Strength training, including weightlifting, can play a vital role in maintaining and building muscle mass, even as we age. Weight training involves using various resistance exercises, such as lifting weights or using resistance machines, to target specific muscle groups.
When we lift weights, we create microscopic tears in our muscle fibers. In response to these tears, our body repairs and rebuilds the muscle fibers, resulting in muscle growth and increased strength. This process iof breakdown, repair, and muscle growth is called Hypertrophy.
Weight training not only enhances hypertrophy, but it also improves mobility, balance, muscle strength, and endurance. As we age, our muscle strength naturally decreases, making daily activities more challenging. However, incorporating weightlifting into our fitness routine can help combat this decline, allowing us to maintain strength and independence. It can also support bone health, improve balance and coordination, boost metabolism, and enhance overall physical function. It's a whole-body workout that targets multiple muscle groups, including the lower body, upper body, and core.
By incorporating weightlifting into our training program, we can effectively combat aging and improve our overall quality of life as we age.

Turning the Tides: Weightlifting for the Elderly
While weightlifting is beneficial for individuals of all ages, it can be especially transformative for older lifters. Weightlifting for the elderly involves tailoring training programs and exercises to meet the unique needs of older adults.
Weightlifting isn't just for the young; it's for anyone who is looking to improve their strength, mobility, and overall health. Whether you're new to weightlifting or have been training for years, there are specific considerations and safety measures that older lifters should take into account.
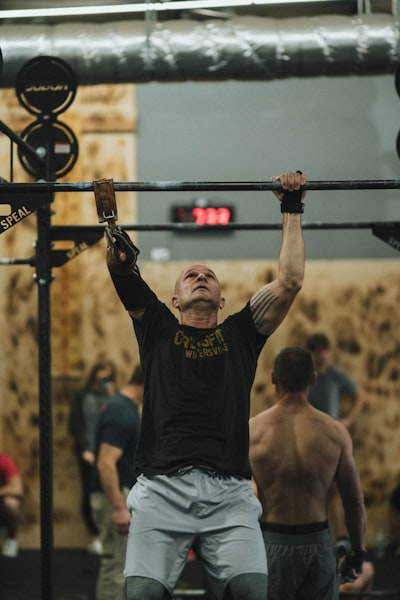
Safety Measures for Older Weightlifters
When it comes to weightlifting, safety should always be a top priority, especially for older lifters. Below are some essential safety measures older weightlifters should follow:
-
Warm-up exercises: Begin every weightlifting session with a proper warm-up routine. This can include dynamic stretches, bodyweight exercises, or light cardio to increase blood flow, warm up the muscles, and reduce the risk of injury.
-
Seek guidance from a physical therapist: If you are new to weightlifting or have any pre-existing conditions, it's important to consult with a physical therapist who can provide personalized guidance and recommendations.
-
Focus on form and technique: Proper form and technique are crucial for older weightlifters to prevent injuries and maximize the benefits of each exercise. Take the time to learn and practice correct form, and consider working with a qualified trainer or coach to ensure you are performing exercises safely and effectively.
-
Stretching routines: Incorporate stretching exercises into your weightlifting routine to improve mobility, flexibility, and range of motion. This can help prevent muscle imbalances, reduce muscle stiffness, and improve overall exercise performance.
-
Listen to your body: Pay attention to any pain, discomfort, or unusual sensations during your weightlifting sessions. If something doesn't feel right, it's important to listen to your body and make modifications or seek professional guidance if needed.
- Remember, it's essential to prioritize safety when engaging in weightlifting, especially as we age. By following these safety measures, older lifters can reduce the risk of injury and train more effectively.
Selecting Appropriate Exercises
When it comes to weightlifting for the elderly, it's important to select exercises that are safe, effective, and tailored to the individual's needs and goals. Below are some tips for selecting appropriate exercises:
-
Focus on lower body exercises: Lower body strength is crucial for mobility and daily activities. Incorporate exercises such as squats, lunges, and leg press to target the major muscle groups in the lower body, including the quads, hamstrings, and glutes.
-
Include upper body exercises: Strengthening the upper body is equally important, as it supports overall balance and functional strength. Consider exercises like bench press, dumbbell curls, and shoulder presses to target the chest, biceps, and shoulders.
-
Incorporate bodyweight exercises: Bodyweight exercises can be a great addition to weightlifting workouts, especially for older lifters who may be new to strength training or are looking for low-impact options. Push-ups, bodyweight squats, and planks can help improve strength and flexibility.
-
Take advantage of resistance bands: Resistance bands are versatile tools that can add variety and challenge to weightlifting routines. They can be used to target specific muscle groups, offer resistance throughout the entire range of motion, and accommodate different strength levels.
-
Emphasize functional movements: Incorporate exercises that mimic real-life movements, such as carrying groceries, getting up from a seated position, or lifting objects from the floor. Functional training helps improve strength and stability in everyday activities.
- By including a variety of lower body, upper body, bodyweight, and resistance band exercises, older lifters can create a balanced weightlifting routine that targets all major muscle groups and promotes overall strength and mobility.
Determining the Right Weight and Intensity
Determining the right weight and intensity for weightlifting workouts is crucial for older lifters to maximize their results and minimize the risk of injury. Here are some guidelines to consider:
-
Tailor weight loads to individual strength levels: Start with a weight that allows you to perform exercises with good form and range of motion, while still feeling challenged. Gradually increase the weight as your strength and comfort levels improve.
-
Focus on moderate weight and high reps: For older lifters who are new to weightlifting or looking to build muscle endurance, using moderate weight with higher repetitions can be effective. Aim for 10-15 repetitions per set, focusing on maintaining proper form throughout each rep.
-
Experienced lifters: heavy loads and muscular failure: If you have been weightlifting for some time and have built a solid foundation of strength, incorporating heavy loads and training to muscular failure can promote muscle hypertrophy (growth). This involves lifting weights that are challenging enough to cause muscle fatigue within 8-12 repetitions.
-
Adjust intensity based on physical condition and training experience: Each individual's physical condition and training experience will vary, so it's important to listen to your body and adjust the weight and intensity of your workouts accordingly. Push yourself to a level that is challenging, but not to the point of pain or discomfort.
- Finding the right weight and intensity for weightlifting is a process of trial and error, but it's essential to listen to your body, use proper form, and gradually progress over time. Consult with a trainer or fitness professional if you need guidance on weight selection or workout intensity.
Deciding Your Workout Frequency
The frequency of weightlifting workouts is an important consideration for older lifters, as it impacts muscle recovery, strength gains, and overall training progress. Here are some factors to consider when deciding on your workout frequency:
-
Aim for 2-3 weight training sessions per week: For older lifters, aiming for 2-3 weight training sessions per week is a good starting point. This allows for adequate muscle recovery while still providing enough stimulus for strength gains.
-
Allow for rest days between weight lifting sessions: Rest days are vital for muscle recovery and growth, especially as we age. Give your muscles time to repair and rebuild by scheduling rest days between weight lifting sessions.
-
Utilize recovery techniques: Incorporating recovery techniques such as foam rolling, active recovery exercises, and quality sleep can enhance muscle recovery, reduce muscle soreness, and improve overall training performance.
-
Balance weight training with cardio exercises: While weightlifting is beneficial for building muscle mass and strength, it's important to balance it with cardio exercises for overall cardiovascular health. Aim for 2-3 days of moderate-intensity cardio, such as brisk walking or cycling, to complement your weight training routine.
-
Vary workout intensity and frequency: To prevent training plateaus and keep your body continuously adapting, consider varying the intensity and frequency of your workouts. Incorporate higher intensity days and lower intensity recovery days to challenge your body in different ways.
- By finding the right balance of workout frequency and incorporating recovery techniques, older lifters can maximize the benefits of weight training while avoiding overtraining and promoting muscle recovery.
Nutrition and Recovery: Key Pillars of Healthy Aging
In addition to weightlifting, nutrition and recovery play crucial roles in supporting healthy aging and muscle maintenance. Proper nutrition provides the building blocks necessary for muscle repair, growth, and overall well-being, while recovery techniques optimize muscle recovery and promote physical performance. Let's dive deeper into the importance of nutrition and recovery for older lifters.

The Importance of High Protein Intake
Achieving and maintaining muscle mass becomes increasingly important as we age, and adequate protein intake is essential for muscle gain and tissue repair. Older lifters, in particular, may benefit from a slightly higher protein intake to support muscle building and weight loss efforts.
Protein is made up of amino acids, which are the building blocks of muscle tissue. When we consume protein, our body breaks it down into individual amino acids, which are then used to repair and build new muscle fibers. Without sufficient protein, our body may struggle to recover from workouts and build muscle mass.
Research has shown that consuming 25-30 grams of protein per meal is optimal for muscle gain and maintenance. This can be achieved through a combination of lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
In addition to supporting muscle growth, a high protein intake can also aid in weight loss by increasing satiety and boosting metabolism. Protein requires more energy to digest, absorb, and metabolize compared to carbohydrates and fats, which can help increase calorie expenditure and promote weight loss.
When considering your protein intake, it's important to focus on quality sources of protein and distribute your intake evenly throughout the day. This ensures a steady supply of essential amino acids for muscle repair and growth. That's why we formulated our Whey Protein to give you the fastest, most convenient, affordable, and highest quality protein you can easily add to your delicious daily routine.
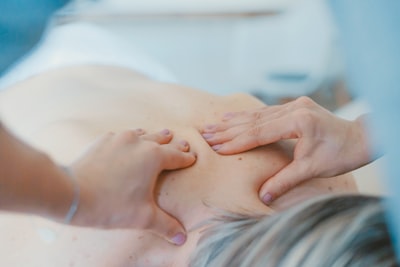
Recovery Techniques for Mature Lifters
Recovery is an essential aspect of any training program, especially for mature lifters. Proper recovery techniques not only support muscle repair and growth, but they also enhance physical performance and reduce the risk of injury. Here are some recovery techniques to consider:
-
Quality sleep: Prioritize good sleep hygiene by establishing a consistent sleep routine, creating a sleep-friendly environment, and aiming for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. During sleep, the body repairs and regenerates muscle tissue, allowing for optimal recovery and growth.
-
Maintain range of motion: Incorporate mobility exercises, such as dynamic stretches, yoga, or Pilates, into your recovery routine to improve joint range of motion, reduce muscle stiffness, and enhance overall flexibility.
-
Foam rolling: Use a foam roller to perform self-myofascial release, targeting specific muscle groups to alleviate muscle tension, improve muscle tissue quality, and prevent muscle imbalances.
-
Active recovery exercises: Engage in low-impact activities, such as swimming, cycling, or gentle walking, on rest days or as part of your recovery routine. These activities increase blood flow, help flush out metabolic waste, and promote muscle recovery.
Significance of Mobility Exercises
Mobility exercises are crucial for older lifters as they help maintain joint range of motion, improve flexibility, and prevent injuries. These exercises focus on improving muscular strength, flexibility, and control, promoting overall mobility and functional movement. Here's why mobility exercises are significant for older lifters:
-
Dynamic stretches: Incorporate dynamic stretches, such as leg swings, arm circles, and hip rotations, into your warm-up routine. These movements help increase blood flow, warm up the muscles, and improve range of motion.
-
Maintain joint range of motion: As we age, our joints can become stiff and lose their full range of motion. Performing mobility exercises, such as shoulder circles, ankle pumps, and spinal twists, can help maintain and improve joint mobility.
-
Improve overall flexibility: Regular mobility exercises can improve muscle flexibility, making everyday activities easier and reducing the risk of muscle strains or injuries.
-
Enhance range of motion: By focusing on exercises that target a wide range of motion, such as lunges, squats, and shoulder presses, older lifters can improve their joint mobility and functional strength.
-
Prevent injuries: Incorporating mobility exercises can help prevent muscle imbalances, reduce the risk of injuries, and improve exercise performance. By maintaining flexibility and range of motion, older lifters can perform weightlifting exercises with better form and technique, minimizing the risk of strain or injury.
- By including mobility exercises in your training routine, you can enhance your flexibility, range of motion, and overall physical performance, allowing you to lift weights more effectively and safely.
Creating a Tailored Workout Plan
Now that we've covered the importance of weightlifting, safety measures, exercise selection, and recovery techniques, it's time to create a tailored workout plan that suits your individual needs and goals. A well-designed training program will maximize results, minimize the risk of injury, and keep you motivated throughout your fitness journey.
Sample Weight Training Workouts
Here are some sample weight training workouts to get you started:
Workout 1: Full-Body Dumbbell Routine
-
Dumbbell squats: 3 sets of 12 reps
-
Dumbbell bench press: 3 sets of 10 reps
-
Dumbbell rows: 3 sets of 12 reps
-
Dumbbell shoulder press: 3 sets of 10 reps
-
Dumbbell bicep curls: 3 sets of 12 reps
- Workout 2: Upper Body Focus with Barbell
-
Bench press: 3 sets of 8-10 reps
-
Barbell rows: 3 sets of 10 reps
-
Overhead press: 3 sets of 8-10 reps
-
Close grip bench press: 3 sets of 10 reps
-
Barbell bicep curls: 3 sets of 12 reps
- Workout 3: Lower Body Emphasis with Leg Press
-
Leg press: 3 sets of 10-12 reps
-
Dumbbell lunges: 3 sets of 10 reps per leg
-
Romanian deadlifts: 3 sets of 10 reps
-
Calf raises: 3 sets of 12-15 reps
-
Plank: Hold for 30-60 seconds, 3 sets
- Feel free to adjust the weight, reps, and sets based on your strength and comfort levels. Remember to focus on maintaining proper form throughout each exercise, and take rest days between your weight training sessions to allow for muscle recovery.
Recommended Cardio/Conditioning Routines
In addition to weight training, cardiovascular exercise is important for overall health, endurance, and weight management. Here are some recommended cardio and conditioning routines for older lifters:
-
High-intensity interval training (HIIT): HIIT involves alternating periods of high-intensity exercise with periods of low-intensity or rest. This type of training can be a great way to improve cardiovascular fitness, burn calories, and boost metabolism. Examples of HIIT exercises include sprinting, jump squats, and burpees.
-
Outdoor activities: Take advantage of outdoor activities like hiking, cycling, or swimming. These activities not only provide cardio benefits but also allow you to enjoy nature and fresh air.
-
Circuit training: Circuit training combines strength training exercises with short bursts of cardio, providing a comprehensive full-body workout. Set up a circuit with exercises such as jumping jacks, mountain climbers, push-ups, lunges, and squat jumps, performing each exercise for a set period of time before moving on to the next.
-
Low-impact cardio options: If you prefer lower-impact cardio exercises, try activities like walking, swimming, cycling, or using the elliptical machine. These exercises are easier on the joints while still providing cardiovascular benefits.
-
Variety is key: Incorporate a variety of cardio exercises into your routine to prevent boredom and challenge different muscle groups. Mix up your cardio workouts by trying new exercises, joining group fitness classes, or incorporating different types of cardio equipment at the gym.
- By including regular cardio and conditioning routines, older lifters can improve their endurance, cardiovascular health, and overall fitness levels, complementing the strength gained from weightlifting.
Long-term Health Optimization Tips for Over 40s
Achieving and maintaining long-term health should be a top priority for individuals over 40, and weightlifting can play a significant role in this journey. Here are some tips for long-term health optimization:
Setting Realistic Expectations
When it comes to weightlifting and fitness over 40, it's important to set realistic expectations. While weightlifting can lead to significant improvements in strength, muscle mass, and overall physical well-being, it's essential to recognize that progress takes time and effort.
Setting unrealistic expectations can lead to disappointment and frustration, which may cause individuals to give up on their fitness goals altogether. Instead, focus on the process and the positive changes you're making in your body and overall health.
The Power of Patience and Persistence
Patience and persistence are key virtues to cultivate when embarking on any fitness journey, especially as we age. It's important to remember that building strength, muscle, and achieving long-term success takes time.
Learning to Listen to Your Body
One of the most important lessons for older lifters is to listen to their bodies. As we age, it becomes increasingly important to pay attention to physical cues and adjust training intensity and techniques accordingly.
The Balance between Challenge and Comfort
Finding the balance between challenge and comfort is crucial for optimal results in weightlifting and overall fitness over 40. Pushing yourself outside of your comfort zone is necessary for progress, but it's equally important to respect your body's limitations and avoid overexertion.
Is Age Just a Number in Weightlifting?
The question of whether age is just a number in weightlifting is a common one, and the answer may surprise you. While age can present certain challenges, weightlifting can still yield significant benefits for older lifters, similar to young peopl.
Lessons from Successful Older Weightlifters.
Successful older weightlifters consistently maintain their training routine, prioritizing recovery for injury prevention and muscle growth. Nutrition is key, with a balanced diet and sufficient protein intake. A positive mindset and adaptability are crucial for success. Safety is paramount, as older weightlifters prioritize proper form and listening to their bodies to avoid injury. Following these principles, older weightlifters can excel in their weightlifting journey well into their 40s and beyond.
Conclusion
In conclusion, age should never be a barrier to achieving your fitness goals. With the right approach and mindset, you can maintain and even build muscle mass well into your 40s and beyond. Weightlifting is a powerful tool that can help counteract the natural muscle deterioration that comes with age. By following safety measures, selecting appropriate exercises, and determining the right weight and intensity for your workouts, you can effectively challenge your muscles and stimulate growth. Additionally, nutrition and recovery play crucial roles in healthy aging. Prioritize high protein intake, incorporate recovery techniques, and include mobility exercises to support your muscles and joints. Lastly, remember to set realistic expectations, be patient and persistent, listen to your body, and find the balance between challenge and comfort. Age is just a number when it comes to weightlifting, and with the right strategies, you can defy the effects of time and continue to build a strong, resilient body.
Links:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30649897/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30649897/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30649897/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21449785/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18268815/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28514618/
https://progensupplements.com/blogs/news/98226497-sometimes-we-need-a-break
https://progensupplements.com/blogs/news/85602945-what-is-the-best-cardio-for-fat-loss
https://progensupplements.com/blogs/news/86388097-10-tips-for-choosing-a-personal-trainer